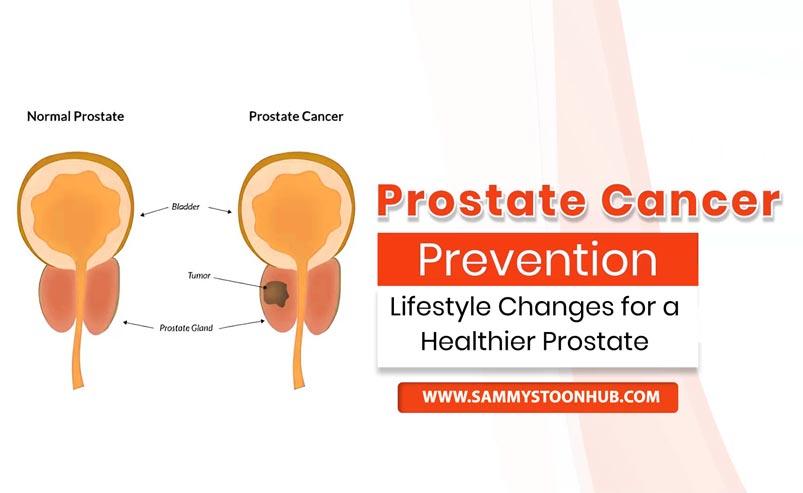
Prostate cancer is a prevalent malignancy among men, particularly those exceeding fifty years of age. While certain immutable risk factors, such as chronological age, genetic predisposition, and familial history, exist, men can adopt several proactive measures to mitigate their risk of developing prostate cancer. This article provides a detailed exposition of evidence-based strategies for prostate cancer prevention, encompassing lifestyle modifications, dietary guidelines, and medical interventions.
Understanding Predisposing Factors for Prostate Cancer
Prior to delving into preventive strategies, it is pertinent to comprehend the risk factors associated with prostate cancer:
- Age: The incidence of prostate cancer exhibits a marked increase in men beyond fifty years of age.
- Family History: A familial history of prostate cancer, specifically in a father or brother, is associated with a twofold increase in risk.
- Race/Ethnicity: Men of African-American descent are identified as a higher-risk demographic. In the United States, for example, Black men are about 70% more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer and are more than twice as likely to die from the disease compared to White men.
- Genetics: Inherited genetic mutations, including but not limited to BRCA1 and BRCA2, may elevate individual susceptibility.
- Lifestyle Factors: Suboptimal dietary habits, obesity, and physical inactivity are recognized as potential contributors to elevated risk.
While certain determinants are non-modifiable, the adoption of a health-conscious lifestyle and informed decision-making can significantly contribute to the reduction of prostate cancer risk.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prostate Cancer Risk Mitigation
Weight Management
- Obesity has been correlated with an increased incidence of aggressive prostate cancer. Excess adipose tissue may promote inflammatory processes and hormonal imbalances, potentially fostering cancer development.
- Maintenance of a body mass index (BMI) within the normative range of 18.5–24.9 is advisable. Regular physical exercise and adherence to a balanced dietary regimen are crucial for achieving and sustaining a healthy weight.
Regular Physical Exercise
- Engagement in physical activity has been demonstrated to correlate with a reduced risk of prostate cancer and confer overall health benefits.
- It is recommended to engage in a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise (e.g., brisk ambulation, cycling) or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise (e.g., running, swimming) per week.
- Resistance training exercises, such as weightlifting, may also offer beneficial effects.
Smoking Cessation
- Tobacco smoking is an established risk factor for numerous malignancies, including prostate cancer. Smoking cessation is associated with improvements in overall health and a reduction in cancer risk.
- Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or participating in smoking cessation programs may be beneficial for individuals seeking to discontinue smoking.
Moderation of Alcohol Consumption
- Excessive alcohol intake has been implicated in a potential increase in prostate cancer risk. It is advisable for men to limit alcohol consumption to a maximum of two standard alcoholic drinks per diem.
Health Benefits of Garcinia Kola
Dietary Recommendations for Prostate Cancer Prevention
Plant-Centric Dietary Approach
- A dietary pattern characterized by a high proportion of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provides essential micronutrients and antioxidants that may exert a protective effect against cancer.
- Cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and kale, contain bioactive compounds like sulforaphane, which possess antineoplastic properties.
- Tomatoes are a rich source of lycopene, an antioxidant that has been associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer.
Selection of Healthful Fats
- Substitution of saturated and trans fats, commonly found in red meat and processed food products, with healthier lipid sources, such as those present in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, is recommended.
- Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, prevalent in fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel) and flaxseeds, may also confer protective benefits.
Limitation of Red and Processed Meat Intake
- Elevated consumption of red meat (e.g., beef, pork) and processed meats (e.g., bacon, sausages) has been correlated with an increased risk of prostate cancer.
- Prioritization of lean protein sources, including poultry, fish, and plant-derived proteins (e.g., beans, lentils), is advisable.
Incorporation of Soy and Green Tea
- Soy-based products, such as tofu and edamame, contain isoflavones, which may contribute to prostate cancer risk reduction.
- Green tea is abundant in polyphenolic compounds, antioxidants that have demonstrated the capacity to inhibit cancer cell proliferation in laboratory studies.
Maintenance of Hydration
- Adequate water intake is conducive to overall physiological function and may facilitate the elimination of metabolic waste products from the body.
Unveiling the Health Benefits of Bananas.
Medical Interventions and Screening Protocols
Routine Health Assessments
- Men aged fifty years and older, or those with elevated risk profiles, should engage in discussions with their healthcare providers regarding prostate cancer screening.
- Standard screening protocols typically involve a Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) assay and a Digital Rectal Examination (DRE).
Awareness of Familial Medical History
- Individuals with a family history of prostate cancer should inform their physicians. Earlier initiation of screening or more frequent surveillance may be indicated in such cases.
Consideration of Genetic Counseling
- Men with a significant familial predisposition to prostate cancer or other malignancies (e.g., breast, ovarian cancer) may derive benefit from genetic counseling to ascertain the presence of inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2.
The potential health risks to your children from not removing your shoes indoors.
Dietary Supplements and Vitamins: Efficacy Considerations
While a well-balanced diet remains the optimal source of nutritional intake, certain dietary supplements may potentially contribute to prostate cancer risk reduction:
- Vitamin D: Lower serum levels of vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. Assessment of vitamin D status and supplementation, if warranted, may be considered.
- Selenium and Vitamin E: Select studies suggest that these antioxidants may possess protective properties. However, excessive supplementation may be detrimental. Medical consultation is advised prior to initiating any supplement regimen.
Stress Management and Psychological Well-being
Chronic psychological stress and compromised mental health may exert immunosuppressive effects and promote systemic inflammation, potentially elevating cancer risk. Incorporation of stress-attenuating practices into daily routines is advisable. Examples include:
- Meditation or mindfulness-based practices.
- Yoga or Tai Chi.
- Recreational activities in natural environments or engagement in avocational pursuits.
Conclusion
Prostate cancerprevention is predicated upon a holistic approach encompassing salutary lifestyle choices, regular medical evaluations, and cognizance of individual risk determinants. By maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a nutrient-dense diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and abstaining from deleterious habits such as smoking, men can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing prostate cancer. Early detection through recommended screening protocols is also of paramount importance, particularly for those with a pertinent family history or other risk factors. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended to formulate a personalized preventive strategy tailored to individual needs. Proactive measures undertaken in the present may yield substantial benefits for long-term health maintenance.
Disclaimer:This article is intended for informational purposes and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and to address any health concerns.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *