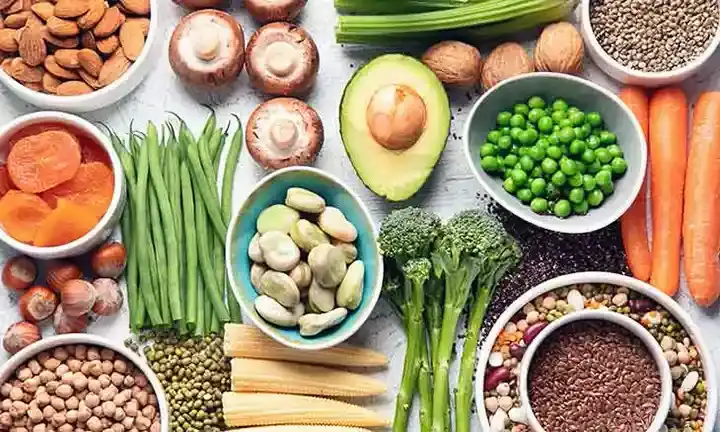
The Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet.
A plant-based diet, which focuses on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and nuts, offers a range of health benefits. It can help improve heart health, manage weight, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
In recent years, the plant-based diet has garnered increasing attention, being hailed as a healthier and more sustainable alternative to traditional diets centered around animal products. The plant-based diet focuses on the consumption of whole plant foods, such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while excluding or minimizing animal-derived products like meat, dairy, and eggs. Numerous studies have highlighted the potential benefits of adopting a plant-based diet, ranging from improved health outcomes to environmental sustainability. This article delves into the key benefits of a plant-based diet, including its effects on physical health, weight management, chronic disease prevention, and the environment.
1. Improved Heart Health
One of the most significant benefits of a plant-based diet is its positive impact on cardiovascular health. Research consistently demonstrates that plant-based diets are associated with lower levels of cholesterol, blood pressure, and a reduced risk of heart disease. Whole plant foods are naturally low in saturated fats, which are primarily found in animal products, and high in fiber, which helps lower cholesterol levels. Additionally, plant-based diets are rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, which combat oxidative stress and inflammation—both of which contribute to the development of heart disease.
Several studies have shown that individuals who adhere to a plant-based diet tend to have a lower incidence of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions compared to those who consume a diet high in animal products. A large-scale study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that people who ate plant-based foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, had a significantly lower risk of developing heart disease than those who consumed a standard Western diet high in meat and processed foods.
2. Weight Management and Obesity Prevention
Another major benefit of a plant-based diet is its role in weight management. Plant-based foods, particularly fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, are typically low in calories and high in fiber, which promotes satiety and helps prevent overeating. Fiber also plays a critical role in maintaining healthy digestion, reducing the risk of constipation, and supporting healthy gut microbiota.
Several studies have indicated that people who follow a plant-based diet tend to have a lower body mass index (BMI) and a reduced risk of obesity compared to individuals who consume a more traditional, meat-heavy diet. One study published in Obesity Reviews found that individuals on plant-based diets had a lower calorie intake and greater weight loss compared to those following diets high in animal products. This suggests that switching to a plant-based diet can be an effective approach for those looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight.
3. Chronic Disease Prevention

A plant-based diet has also been linked to the prevention and management of various chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers. The high fiber content in plant-based foods helps regulate blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, plant-based diets are often rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, which can help prevent or manage conditions such as arthritis and autoimmune diseases.
For instance, research has shown that a plant-based diet can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. A study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that individuals who followed plant-based diets had a 23% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those who ate a diet high in animal products. Furthermore, the abundance of phytonutrients in plant foods, including antioxidants and polyphenols, plays a crucial role in protecting the body from cellular damage that could lead to cancer.
4. Improved Digestive Health

A plant-based diet is highly beneficial for digestive health, largely due to its high fiber content. Fiber is an essential nutrient that supports the proper functioning of the digestive system. It helps regulate bowel movements, prevents constipation, and reduces the risk of gastrointestinal disorders such as diverticulitis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and colorectal cancer. Moreover, a diet rich in plant-based foods can promote a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for overall digestive health and immune system function.
The consumption of diverse plant-based foods supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, leading to improved digestion and a more balanced gut flora. Studies have shown that people who consume plant-based diets have a higher diversity of gut bacteria, which is associated with a healthier digestive system.
5. Environmental Sustainability

In addition to the health benefits, a plant-based diet contributes to environmental sustainability. The production of plant-based foods generally requires fewer natural resources, such as land, water, and energy, compared to the farming and processing of animal products. Livestock farming is a leading cause of greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and habitat loss, making it a major contributor to climate change.
By shifting toward a plant-based diet, individuals can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and environmental impact. Research published by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization found that plant-based diets have a considerably lower environmental impact in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to meat-based diets. Adopting a plant-based lifestyle not only benefits personal health but also promotes the conservation of natural resources and helps mitigate the effects of climate change.
6. Improved Mental Health and Well-being

Emerging research suggests that plant-based diets can positively influence mental health and overall well-being. Plant-based foods, particularly fruits and vegetables, are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which have been shown to have a protective effect against mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and stress.
Certain nutrients found in plant-based foods, including omega-3 fatty acids (found in flaxseeds and walnuts) and folate (found in leafy greens and legumes), have been associated with improved mood and cognitive function. Additionally, plant-based diets often focus on nutrient-dense foods, which support brain health by providing the necessary nutrients to promote neuroplasticity and overall cognitive function.
Conclusion
A plant-based diet offers a wide array of health benefits, including improved heart health, weight management, chronic disease prevention, better digestive health, and mental well-being. Furthermore, the environmental advantages of adopting a plant-based lifestyle—such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions and less resource consumption—make it an appealing choice for individuals looking to lead a more sustainable lifestyle. As research continues to unfold, the evidence supporting the numerous advantages of plant-based eating continues to grow, making it a viable and attractive option for those seeking to improve their health and contribute to the well-being of the planet.
Adopting a plant-based diet, even in part, can be a step toward a healthier and more sustainable future. Whether driven by personal health goals or environmental concerns, the benefits of plant-based eating are undeniable.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


