Anxiety Management Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide.
Eight Approaches to Facilitate Effective Anxiety Management.
Anxiety is a natural response to stress, but when it becomes chronic or overwhelming, it can affect one’s ability to function effectively in daily life. Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health conditions worldwide, and they come in many forms, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety, panic disorder, and phobias. Fortunately, there are numerous techniques available to help manage anxiety, ranging from lifestyle changes and relaxation strategies to cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT). This article delves into various effective anxiety management techniques that can empower individuals to regain control over their mental well-being.
1. Mindfulness and Meditation

Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment and accepting it without judgment. Practicing mindfulness can help reduce anxiety by shifting the focus away from worrisome thoughts about the future or past. Research has shown that mindfulness meditation can help decrease anxiety symptoms by training the brain to be more aware of thoughts and feelings in a non-reactive way.
Techniques:
- Mindful Breathing: Pay attention to each inhale and exhale, and bring your focus back to your breath when your mind wanders.
- Body Scan Meditation: Involves mentally scanning your body from head to toe, noticing any tension or discomfort and consciously relaxing those areas.
- Guided Meditation: Using audio or apps to follow a guided meditation session can help beginners stay on track.
Benefits: Regular mindfulness practice can lower heart rate, reduce stress, and improve emotional regulation, providing relief from anxiety.
2. Deep Breathing Exercises

Breathing exercises are one of the simplest yet most effective techniques to reduce immediate anxiety. The body's stress response often leads to rapid, shallow breathing, which can exacerbate feelings of panic. Slow, controlled breathing activates the body’s relaxation response, reducing anxiety levels.
Techniques:
- Box Breathing (Square Breathing): Inhale for four counts, hold your breath for four counts, exhale for four counts, and hold again for four counts.
- 4-7-8 Breathing: Inhale through the nose for a count of four, hold for seven counts, and exhale slowly through the mouth for eight counts.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Breathe deeply from the diaphragm, not the chest, ensuring that the stomach rises and falls rather than the chest.
Benefits: These exercises help activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which counteracts the effects of stress and anxiety.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
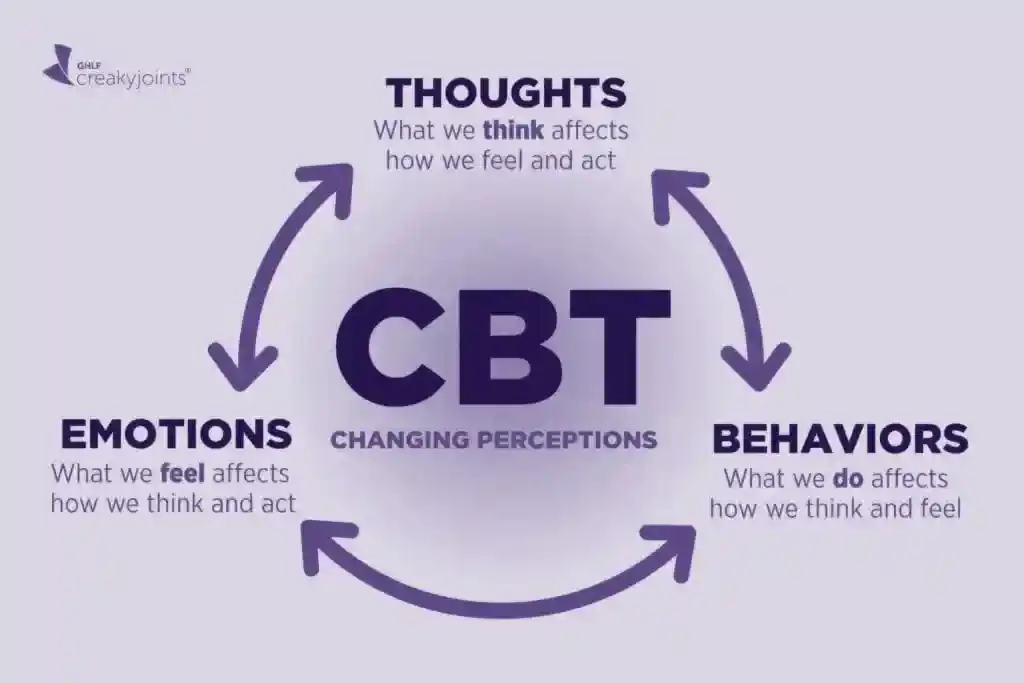
CBT is a well-established, evidence-based therapy that helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. It teaches individuals to recognize irrational thoughts and replace them with more realistic and positive thinking. CBT also includes practical tools to manage stress and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Key Components:
- Cognitive Restructuring: Identifying and challenging distorted thoughts that fuel anxiety, such as catastrophizing or overgeneralizing.
- Behavioral Activation: Encouraging individuals to engage in positive activities that bring joy or fulfillment, thus reducing the time spent focusing on anxious thoughts.
- Exposure Therapy: Gradual exposure to feared situations, allowing individuals to reduce avoidance behavior and build resilience over time.
Benefits: CBT equips individuals with practical tools to manage anxiety in a lasting way, promoting better thought patterns and emotional responses.
4. Physical Activity and Exercise
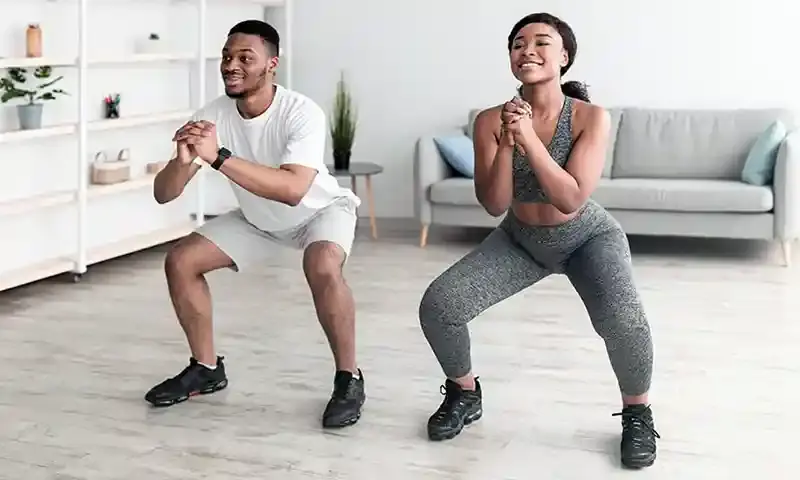

Physical activity is one of the most effective natural remedies for reducing anxiety. Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural mood elevators. Additionally, regular exercise helps improve sleep, boost self-esteem, and reduce overall levels of stress and anxiety.
Effective Activities:
- Aerobic Exercises: Activities like walking, running, or cycling can improve cardiovascular health while reducing anxiety.
- Yoga: Combines deep breathing, mindfulness, and gentle movement to relax the body and mind.
- Strength Training: Lifting weights or performing resistance exercises has been shown to help reduce symptoms of anxiety by boosting confidence and improving physical well-being.
Benefits: Exercise helps break the cycle of worry by allowing the body to focus on movement rather than anxious thoughts, and it also promotes a more positive mindset.
5. Healthy Lifestyle Choices

A balanced lifestyle is critical to managing anxiety. Adequate sleep, proper nutrition, and reducing substances that increase anxiety (like caffeine and alcohol) can significantly improve mental health.
Tips for a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensure 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Avoid caffeine and screens before bedtime, and establish a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a well-rounded diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Low blood sugar and dehydration can exacerbate anxiety.
- Limit Stimulants: High doses of caffeine or alcohol can trigger or heighten anxiety symptoms. Reduce or eliminate these substances if possible.
Benefits: A healthy lifestyle provides the foundation for emotional resilience, making it easier to handle stress and anxiety.
6. Social Support and Talking to Someone
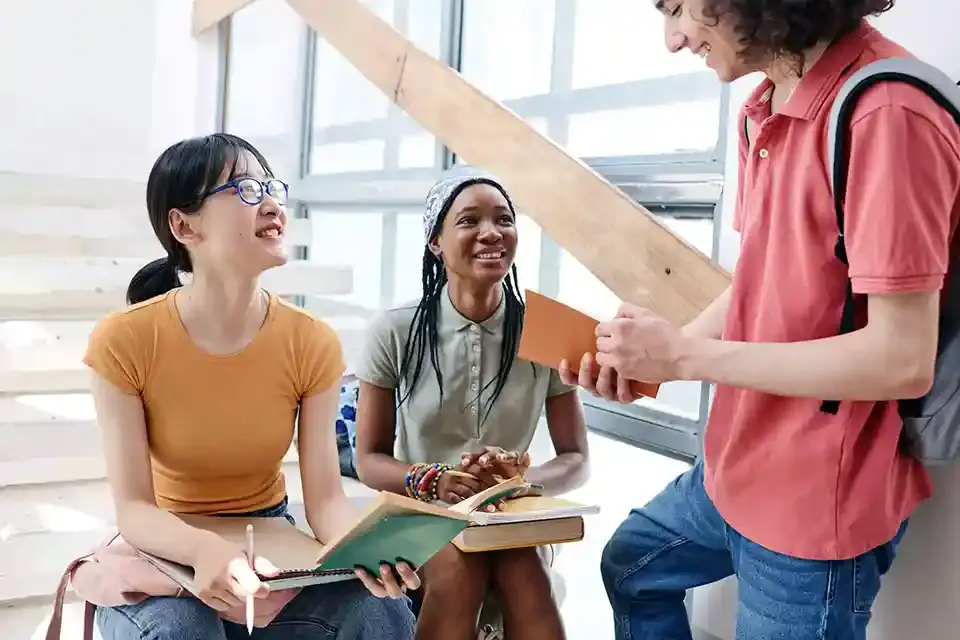

Isolation can worsen anxiety, so it’s crucial to seek support from trusted friends, family members, or a mental health professional. Talking to others about your feelings helps alleviate the burden of anxiety and provides a sense of validation. Group therapy or support groups for anxiety disorders also offer a sense of belonging and shared understanding.
Tips for Connecting:
- Reach Out to a Friend: Sometimes, simply talking about your feelings can help you feel lighter and less burdened.
- Therapy or Counseling: Speaking with a therapist provides professional guidance and coping strategies tailored to your specific anxiety needs.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with others who experience similar challenges can provide comfort and encouragement.
Benefits: Social interaction fosters connection and empathy, making it easier to manage anxiety by providing comfort and shared experiences.
7. Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
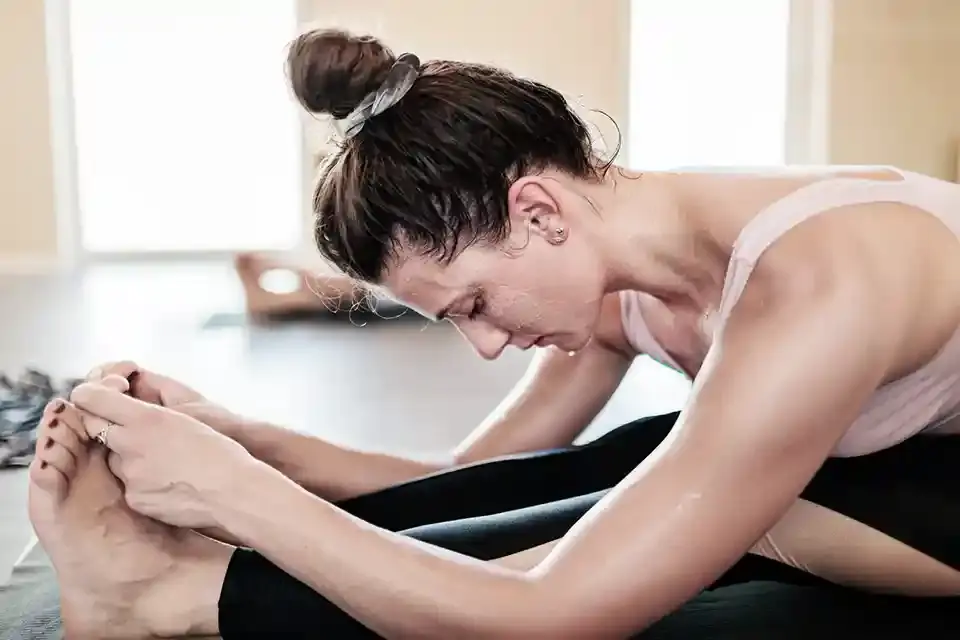

Progressive Muscle Relaxation is a relaxation technique that involves tensing and then releasing various muscle groups in the body. This method helps individuals become more aware of physical tension, which often accompanies anxiety, and learn how to release that tension.
Steps to Practice:
- Begin by tensing the muscles in your feet, holding for a few seconds, and then releasing.
- Gradually work your way up through the body—calves, thighs, abdomen, hands, arms, shoulders, neck, and face—tensing and relaxing each group of muscles.
- Focus on the contrast between tension and relaxation, paying attention to how the muscles feel as they release tension.
Benefits: PMR helps reduce muscle tension and promotes relaxation, aiding in the reduction of anxiety symptoms and improving overall mental calmness.
8. Journaling
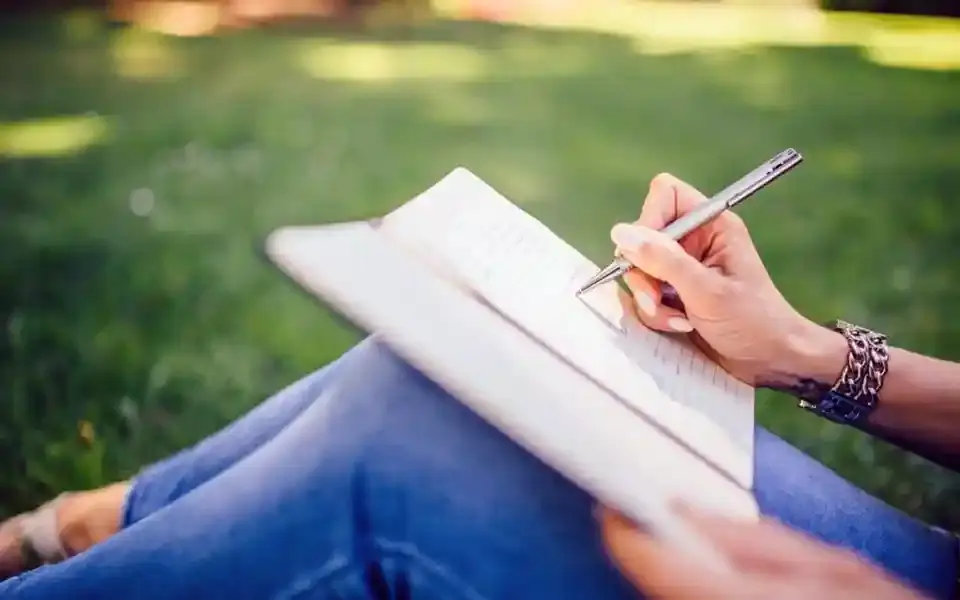

Writing down thoughts and feelings in a journal can help individuals process emotions and gain clarity. Journaling allows for self-reflection and an opportunity to track patterns in anxious thinking, helping individuals to better understand the triggers of their anxiety.
Journaling Prompts:
- Write about a situation that caused you anxiety today and how you reacted to it.
- Identify any irrational thoughts or fears, and write down alternative, more balanced thoughts.
- Reflect on positive aspects of your day and express gratitude for things you are thankful for.
Benefits: Journaling promotes emotional awareness and provides a therapeutic outlet for expressing feelings, helping to release built-up anxiety.
Conclusion
Managing anxiety is a multifaceted process that requires a combination of strategies and techniques tailored to an individual's needs. While some people may benefit from mindfulness practices or therapy, others may find relief in physical activity or lifestyle changes. The key is to explore and adopt the techniques that resonate most and to consistently practice them to build resilience over time. Remember that seeking professional support is a critical step when anxiety becomes overwhelming, and a comprehensive approach can greatly improve one’s quality of life. By employing these techniques, individuals can develop greater emotional regulation, a sense of control, and an overall healthier relationship with anxiety.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


